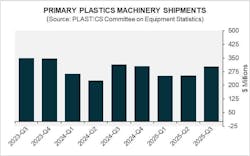
Shipments of plastics processing equipment rise in Q3 2025
Shipments of injection molding and extrusion equipment in the third quarter of 2025 rose 19.5 percent both quarter-over-quarter (Q/Q) and year-over-year (Y/Y), with a total value of $303.2 million, according to the Plastics Industry Association's Committee on Equipment Statistics (CES).
Injection molding machinery shipments jumped 30 percent from the previous quarter and 4.2 percent from a year earlier. But shipments of extrusion equipment fell Q/Q and Y/Y. Single-screw extruders decreased 4.9 percent from the previous quarter and 24.2 percent Y/Y, while twin-screw extruders fell 28.9 percent and 38.6 percent Q/Q and Y/Y, respectively.
“Although shipments continued to increase in the third quarter, it is obvious that both processes faced different headwinds during the quarter. Sector-specific drivers were at play, causing injection molding shipments to rise while those for extrusion fell. Both equipment types were in different cycles,” said Perc Pineda, PLASTICS’ chief economist.
High interest rates have held down residential construction rates, which in turn has suppressed demand for extruded construction supplies. Meanwhile, motor vehicles and parts production have been trending up.
“The 50-basis-point interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve this year — and the market pricing in additional cuts in 2026 — have set the tone for lower borrowing costs ahead, which will eventually feed into plastics manufacturing and lead to higher equipment demand,” Pineda said.
Regarding U.S. plastics machinery trade, based on July data — the latest available due to the government shutdown — exports totaled $112.5 million, while imports totaled $336.1 million, resulting in a $223.5 million trade deficit. Exports decreased by 1.6 percent year over year, while imports fell by 39.1 percent. The trade deficit rose 75.6 percent in July from the same month last year.
At K 2025, where PLASTICS released its annual Global Trends Report, the organization reported that in the first six months of 2025, plastics machinery exports dropped 13 percent, while imports increased 4.5 percent, boosting the machinery trade deficit by 13.1 percent. The report noted that “this sector is being affected by tariff uncertainty and, possibly, by the push to import more machinery and parts ahead of anticipated tariff increases.”
CES also surveys members quarterly about their outlook for the next 12 months. In the Q3 survey, 52 percent of respondents expected market conditions to remain steady or improve, slightly lower than 58 percent in the previous quarter. However, the share reporting that quoting activity held steady or improved rose from 76 percent to 81 percent, the second consecutive quarter of an increase.
“While the government shutdown has delayed the release of economic data, the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta’s GDPNow estimate for third-quarter growth — as of Nov. 5 — stands at 4.0 percent,” Pineda said. “Trade and tariff issues remain a concern, yet markets appear to be adapting to this evolving landscape, which hinges on U.S. policy shifts and outcomes from trade talks with key partners.”