PLASTICS issues Q1 machinery report
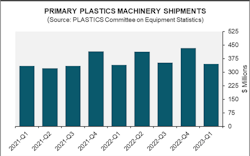
Shipments of primary plastics machinery in North America showed a value of $345.8 million in Q1 2023 — 20.1 percent lower than the previous quarter, but up 1.6 percent compared to the same period last year, according to a report from the Plastics Industry Association’s (PLASTICS’) Committee on Equipment Statistics (CES).
“Despite a weaker economic outlook, plastics machinery shipments managed to show year-on-year growth,” wrote PLASTICS’ Chief Economist, Perc Pineda. “First-quarter shipments were slightly lower than the previous quarter, but this is typically expected as the first quarter tends to have lower shipment volumes. The current first-quarter shipments are comparable to previous quarters during economic expansions.”
The largest decrease in value from the previous quarter among the primary plastics machinery types (injection molding and extrusion) was seen in single-screw extruders, which fell 28.4 percent. They were followed by a 19.9 percent decrease for injection molding shipments, then twin-screw extruders, which declined by 14.7 percent.
However, when comparing Q1 2023 shipments to the Q1 2022 levels, single-screw and twin-screw extruders increased by 11.4 percent and 94.9 percent, respectively. For that same time period, injection molding shipments experienced a 2.7 percent decline.
In its quarterly survey of plastics machinery suppliers’ perspectives, CES found fewer respondents expecting market conditions to remain unchanged or improve in the next quarter, a fall from 35 percent to 33 percent. Those anticipating unchanged or improved conditions in the next 12 months dropped from 45 percent to 38 percent.
U.S. plastics machinery exports experienced a 2.9 percent decrease, amounting to $229.3 million, in the first quarter. Mexico and Canada remained the top export markets for U.S. plastics machinery, with combined exports to these countries totaling $115.6 million, accounting for approximately half (50.4 percent) of total U.S. plastics machinery exports. Meanwhile, imports rose by 6.7 percent in Q1 to reach $535.7 million, increasing the U.S. plastics machinery trade deficit to $306.4 million.
“Despite the U.S. economy displaying resilience and robust household sector spending due to a strong labor market, the implementation of contractionary monetary policy in March 2022 is beginning to impact the financial market and will have broader implications for the manufacturing sector, including the plastics industry,” Pineda wrote.
He noted that the current low unemployment rates — 0.1 percent in plastic and rubber products manufacturing in April — cannot be sustained indefinitely, and that the future trajectory of plastics equipment shipments will continue to depend on U.S. macroeconomic conditions.